- Home
- Plate Heat Exchanger
- Welded Plate Heat Exchanger
What is a Welded Plate Heat Exchanger and How Does It Work
What is a Welded Plate Heat Exchanger
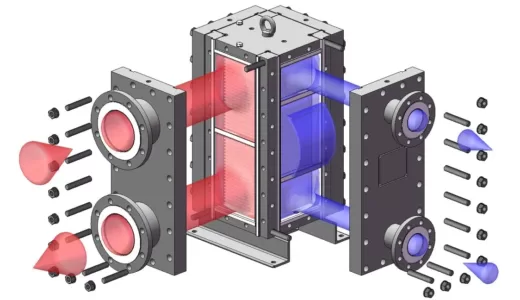
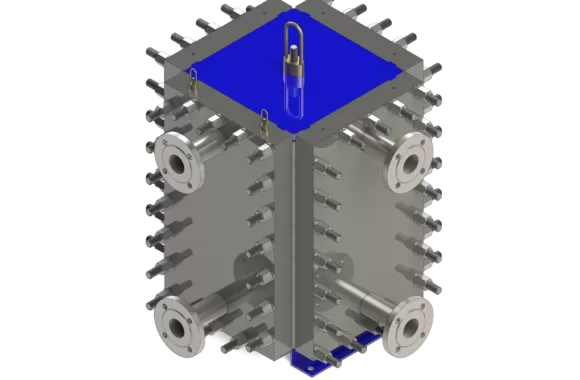
Welded plate heat exchanger is a plate heat exchanger made of a series of corrugated metal plates welded by laser or argon arc welding. The plate group and the plate group are connected by welding with molding strips. Because there is no gasket seal, it has higher temperature and pressure resistance. It can be applied to extreme working conditions of high temperature and high pressure.
Welded plate heat exchangers are divided into non-detachable fully welded plate heat exchangers, 2-sided detachable fully welded plate heat exchangers, 4-sided detachable fully welded plate heat exchangers (HFM bloc), and wide channel fully welded plate heat exchanger.
How Does a Welded Plate Heat Exchanger Work
A welded plate heat exchanger (WPHE) is a type of heat exchanger that uses welded plates to transfer heat between two fluids. Unlike gasketed plate heat exchangers, welded plate heat exchanger do not use gaskets or seals between the plates, which makes them suitable for applications where the leakage is a concern.
The welded plate heat exchanger consists of a series of thin metal plates, which are welded together to form a series of channels or passages. The plates are designed to create a large surface area for heat transfer and are typically made of materials that have high thermal conductivity, such as stainless steel or titanium.
The two fluids that need to be heated or cooled flow through the different passages of the heat exchanger, with each fluid flowing through alternate passages. As the fluids flow past each other, heat is transferred between them through the thin metal plates.
The welded plate heat exchanger design allows for a higher degree of thermal efficiency compared to traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers, as there is less thermal resistance between the fluids and the plates. The lack of gaskets or seals also means that welded plate heat exchanger are less prone to leakage and require less maintenance.
Welded plate heat exchanger are commonly used in applications where high pressures or temperatures are involved, such as in chemical processing, oil and gas production, and power generation. They are also well-suited for applications where the fluids being transferred are corrosive or have a high fouling potential, as the smooth surface of the welded plates makes them less prone to fouling compared to other heat exchanger designs.
Advantages of Welded Plate Heat Exchanger
Fully Welded without Gasket – Prone to leakage, required less maintenance.
High Temperature /Pressure Resistance – Compare to shell and tube heat exchanger
High Heat Exchange Efficiency – less thermal resistance between fluids and plates.
Compact Structure – Welded plate heat exchangers are very compact and take up less space compared to other types of heat exchangers.
Reliable – At HFM, we strictly adhere to the highest standards of quality and safety, ensuring all of our products meet the rigorous requirements of GRG, FDA, and SGS certifications.
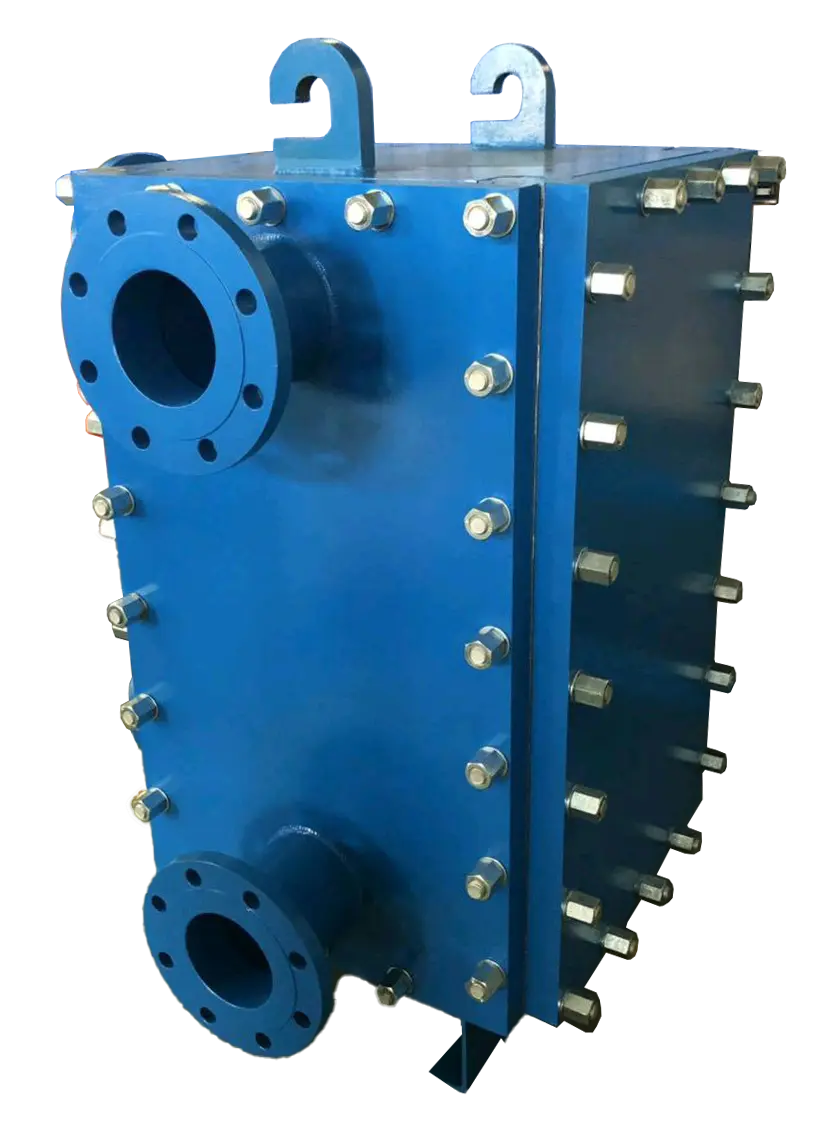

Basic Parameters of Welded Plate Heat Exchanger
Stainless Steel: 304L, 316L, 904L
Special Metals: 254SMO, Hastelloy 276, Titanium, Nickel200/201, etc.
Plate Thickness: 0.8mm-1.2mm
Design Pressure: Max 40bar
Design Temperature: -196° to 400°


Recommended Applications of Welded Plate Heat Exchanger
Petrochemical
Oil & Gas
Energy Power
Metallurgy
Biomedical

